Calculations and property-getters which do not modify the studied quantum state. More...
Functions | |
| qreal | calcDensityInnerProduct (Qureg rho1, Qureg rho2) |
Computes the Hilbert-Schmidt scalar product (which is equivalent to the Frobenius inner product of matrices) of two density matrices rho1 and rho2 of equivalent size. More... | |
| Complex | calcExpecDiagonalOp (Qureg qureg, DiagonalOp op) |
Computes the expected value of the diagonal operator op for state qureg. More... | |
| qreal | calcExpecPauliHamil (Qureg qureg, PauliHamil hamil, Qureg workspace) |
Computes the expected value of qureg under Hermitian operator hamil. More... | |
| qreal | calcExpecPauliProd (Qureg qureg, int *targetQubits, enum pauliOpType *pauliCodes, int numTargets, Qureg workspace) |
| Computes the expected value of a product of Pauli operators. More... | |
| qreal | calcExpecPauliSum (Qureg qureg, enum pauliOpType *allPauliCodes, qreal *termCoeffs, int numSumTerms, Qureg workspace) |
| Computes the expected value of a sum of products of Pauli operators. More... | |
| qreal | calcFidelity (Qureg qureg, Qureg pureState) |
Calculates the fidelity of qureg (a state-vector or density matrix) against a reference pure state (necessarily a state-vector). More... | |
| qreal | calcHilbertSchmidtDistance (Qureg a, Qureg b) |
Computes the Hilbert Schmidt distance between two density matrices a and b, defined as the Frobenius norm of the difference between them. More... | |
| Complex | calcInnerProduct (Qureg bra, Qureg ket) |
Computes the inner product 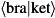 of two equal-size state vectors, given by. More... of two equal-size state vectors, given by. More... | |
| void | calcProbOfAllOutcomes (qreal *outcomeProbs, Qureg qureg, int *qubits, int numQubits) |
Populates outcomeProbs with the probabilities of every outcome of the sub-register contained in qubits. More... | |
| qreal | calcProbOfOutcome (Qureg qureg, int measureQubit, int outcome) |
| Gives the probability of a specified qubit being measured in the given outcome (0 or 1). More... | |
| qreal | calcPurity (Qureg qureg) |
| Calculates the purity of a density matrix, by the trace of the density matrix squared. More... | |
| qreal | calcTotalProb (Qureg qureg) |
A debugging function which calculates the probability of the qubits in qureg being in any state, which should always be 1 for correctly normalised states (hence returning a real number). More... | |
| Complex | getAmp (Qureg qureg, long long int index) |
| Get the complex amplitude at a given index in the state vector. More... | |
| Complex | getDensityAmp (Qureg qureg, long long int row, long long int col) |
| Get an amplitude from a density matrix at a given row and column. More... | |
| qreal | getImagAmp (Qureg qureg, long long int index) |
| Get the imaginary component of the complex probability amplitude at an index in the state vector. More... | |
| long long int | getNumAmps (Qureg qureg) |
Returns the number of complex amplitudes in a state-vector qureg. More... | |
| int | getNumQubits (Qureg qureg) |
Returns the number of qubits represented by qureg. More... | |
| qreal | getProbAmp (Qureg qureg, long long int index) |
| Get the probability of a state-vector at an index in the full state vector. More... | |
| qreal | getRealAmp (Qureg qureg, long long int index) |
| Get the real component of the complex probability amplitude at an index in the state vector. More... | |
Detailed Description
Calculations and property-getters which do not modify the studied quantum state.
Function Documentation
◆ calcDensityInnerProduct()
Computes the Hilbert-Schmidt scalar product (which is equivalent to the Frobenius inner product of matrices) of two density matrices rho1 and rho2 of equivalent size.
That is, we define the Hilbert-Schmidt scalar product
![\[ ((\rho_1, \rho_2))_{HS} := \text{Tr}[ \rho_1^\dagger \rho_2 ], \]](form_148.png)
which is equivalent to the sum of products of matrix elemets, i.e.,
![\[ ((\rho_1, \rho_2))_{HS} = \sum\limits_i \sum\limits_j (\rho_1)_{ij}^* (\rho_2)_{ij} \]](form_149.png)
Assuming that both density matrices are Hermitian, the resulting scalar product is real and invariant under reordering its arguments as
![\[ ((\rho_1, \rho_2))_{HS} = ((\rho_2, \rho_1))_{HS} = \text{Tr}[\rho_1 \rho_2] \]](form_150.png)
If both rho1 and rho2 are density matrices of pure states bra and ket, then the equality holds
![\[ ((\rho_1, \rho_2))_{HS} = |\langle \text{bra} | \text{ket} \rangle|^2. \]](form_151.png)
If either or both of rho1 and rho2 are non Hermitian (i.e. invalid density matrices), then this function returns the real component of the scalar product, and discards the imaginary component. That is, it returns
![\[ \text{Re}\{ \text{Tr}[ \rho_1^\dagger \rho_2 ] \} = \text{Re}\{ \text{Tr}[ \rho_2^\dagger \rho_1 ] \}. \]](form_152.png)
This is still sometimes useful, e.g. in calculating the inner product with an anti-commutator, e.g. (for Hermitian 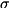 ,
, 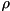 ,
, 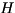 )
)
![\[ ((\sigma, H \rho + \rho H))_{HS} = 2 \; \text{Re} \{ ((\sigma, H \rho))_{HS} \} \]](form_155.png)
where 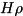 could be a weighted sum of Pauli products applied to
could be a weighted sum of Pauli products applied to 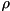 through applyPauliSum().
through applyPauliSum().
- Parameters
-
[in] rho1 qureg as a density matrix (to have its values conjugate transposed) [in] rho2 qureg as a density matrix
- Returns
- the real Hilbert-Schmidt scalar product of density matrices
rho1andrho2(assuming Hermiticity)
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if
rho1andrho2are not both density matrices - if
rho1andrho2have mismatching dimensions
- if
Definition at line 1158 of file QuEST.c.
References densmatr_calcInnerProduct(), validateDensityMatrQureg(), and validateMatchingQuregDims().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ calcExpecDiagonalOp()
| Complex calcExpecDiagonalOp | ( | Qureg | qureg, |
| DiagonalOp | op | ||
| ) |
Computes the expected value of the diagonal operator op for state qureg.
Since op is not necessarily Hermitian, the expected value may be a complex number.
Let 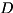 be the diagonal operator
be the diagonal operator op, with diagonal elements 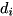 . Then if
. Then if qureg is a state-vector 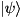 , this function computes
, this function computes
![\[ \langle \psi | D | \psi \rangle = \sum_i |\psi_i|^2 \, d_i \]](form_46.png)
If qureg is a density matrix 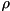 , this function computes
, this function computes
![\[ \text{Trace}( D \rho ) = \sum_i \rho_{ii} \, d_i \]](form_48.png)
- See also
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg a state-vector or density matrix [in] op the diagonal operator to compute the expected value of
- Returns
- the expected vaulue of the operator
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if
opwas not created - if
opacts on a different number of qubits thanquregrepresents
- if
Definition at line 1228 of file QuEST.c.
References densmatr_calcExpecDiagonalOp(), Qureg::isDensityMatrix, statevec_calcExpecDiagonalOp(), and validateDiagonalOp().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ calcExpecPauliHamil()
| qreal calcExpecPauliHamil | ( | Qureg | qureg, |
| PauliHamil | hamil, | ||
| Qureg | workspace | ||
| ) |
Computes the expected value of qureg under Hermitian operator hamil.
Represent hamil as 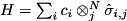 (where
(where 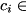
hamil.termCoeffs and 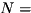
hamil.numQubits). This function computes 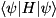 if
if qureg = 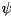 is a state-vector, and computes
is a state-vector, and computes 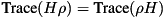 if
if qureg = 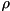 is a density matrix.
is a density matrix.
This function is merely an encapsulation of calcExpecPauliSum() - refer to the doc there for an elaboration.
workspace must be a register with the same type (state-vector vs density matrix) and dimensions (number of represented qubits) as qureg and hamil, and is used as working space. When this function returns, qureg will be unchanged and workspace will be set to qureg pre-multiplied with the final Pauli product in hamil. NOTE that if qureg is a density matrix, workspace will become 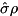 which is itself not a density matrix (it is distinct from
which is itself not a density matrix (it is distinct from 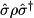 ).
).
This function works by cloning the qureg state into workspace, applying each of the specified Pauli products in hamil to workspace (one Pauli operation at a time), then computing its inner product with qureg (for state-vectors) or its trace (for density matrices) multiplied with the corresponding coefficient, and summing these contributions. It therefore should scale linearly in time with the total number of non-identity specified Pauli operators.
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg the register of which to find the expected value, which is unchanged by this function [in] hamil a PauliHamilcreated with createPauliHamil() or createPauliHamilFromFile()[in,out] workspace a working-space qureg with the same dimensions as qureg, which is modified to be the result of multiplying the state with the final specified Pauli product
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if any code in
hamil.pauliCodesis not a valid Pauli code - if
hamil.numSumTerms<= 0 - if
workspaceis not of the same type and dimensions asquregandhamil
- if any code in
Definition at line 1219 of file QuEST.c.
References PauliHamil::numSumTerms, PauliHamil::pauliCodes, statevec_calcExpecPauliSum(), PauliHamil::termCoeffs, validateMatchingQuregDims(), validateMatchingQuregPauliHamilDims(), validateMatchingQuregTypes(), and validatePauliHamil().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ calcExpecPauliProd()
| qreal calcExpecPauliProd | ( | Qureg | qureg, |
| int * | targetQubits, | ||
| enum pauliOpType * | pauliCodes, | ||
| int | numTargets, | ||
| Qureg | workspace | ||
| ) |
Computes the expected value of a product of Pauli operators.
Letting 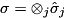 be the operators indicated by
be the operators indicated by pauliCodes and acting on qubits targetQubits, this function computes 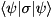 if
if qureg = 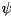 is a state-vector, and computes
is a state-vector, and computes 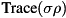 if
if qureg = 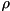 is a density matrix.
is a density matrix.
pauliCodes is an array of length numTargets which specifies which Pauli operators to enact on the corresponding qubits in targetQubits, where 0 = PAULI_I, 1 = PAULI_X, 2 = PAULI_Y, 3 = PAULI_Z. The target qubits must be unique, and at most qureg.numQubitsRepresented may be specified. For example, on a 7-qubit state-vector,
will compute 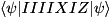 (where in this notation, the left-most operator applies to the least-significant qubit, i.e. that with index 0).
(where in this notation, the left-most operator applies to the least-significant qubit, i.e. that with index 0).
workspace must be a register with the same type (state-vector vs density matrix) and dimensions (number of represented qubits) as qureg, and is used as working space. When this function returns, qureg will be unchanged and workspace will be set to 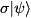 (if
(if qureg is a state-vector) or 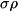 (if
(if qureg is a density matrix). NOTE that this last quantity is NOT the result of applying the paulis as unitaries, 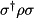 , but is instead the result of their direct multiplication with the density matrix. It is therefore itself not a valid density matrix.
, but is instead the result of their direct multiplication with the density matrix. It is therefore itself not a valid density matrix.
This function works by cloning the qureg state into workspace, applying the specified Pauli operators to workspace then computing its inner product with qureg (for state-vectors) or its trace (for density matrices). It therefore should scale linearly in time with the number of specified non-identity Pauli operators, which is bounded by the number of represented qubits.
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg the register of which to find the expected value, which is unchanged by this function [in] targetQubits a list of the indices of the target qubits [in] pauliCodes a list of the Pauli codes (0=PAULI_I, 1=PAULI_X, 2=PAULI_Y, 3=PAULI_Z) to apply to the corresponding qubits in targetQubits[in] numTargets number of target qubits, i.e. the length of targetQubitsandpauliCodes[in,out] workspace a working-space qureg with the same dimensions as qureg, which is modified to be the result of multiplying the state with the pauli operators
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if
numTargetsis outside [1,qureg.numQubitsRepresented]) - if any qubit in
targetQubitsis outside [0,qureg.numQubitsRepresented)) - if any qubit in
targetQubitsis repeated - if any code in
pauliCodesis not in {0,1,2,3} - if
workspaceis not of the same type and dimensions asqureg
- if
Definition at line 1201 of file QuEST.c.
References statevec_calcExpecPauliProd(), validateMatchingQuregDims(), validateMatchingQuregTypes(), validateMultiTargets(), and validatePauliCodes().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ calcExpecPauliSum()
| qreal calcExpecPauliSum | ( | Qureg | qureg, |
| enum pauliOpType * | allPauliCodes, | ||
| qreal * | termCoeffs, | ||
| int | numSumTerms, | ||
| Qureg | workspace | ||
| ) |
Computes the expected value of a sum of products of Pauli operators.
Let 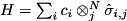 be the operators indicated by
be the operators indicated by allPauliCodes (where 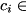
termCoeffs and 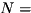
qureg.numQubitsRepresented). This function computes 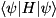 if
if qureg = 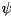 is a state-vector, and computes
is a state-vector, and computes 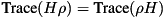 if
if qureg = 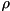 is a density matrix.
is a density matrix.
allPauliCodes is an array of length numSumTerms* specifies which Pauli operators to apply, where 0 = qureg.numQubitsRepresented whichPAULI_I, 1 = PAULI_X, 2 = PAULI_Y, 3 = PAULI_Z. For each sum term, a Pauli operator must be specified for EVERY qubit in qureg; each set of numSumTerms operators will be grouped into a product. termCoeffs is an arrray of length numSumTerms containing the term coefficients. For example, on a 3-qubit state-vector,
will compute 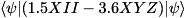 (where in this notation, the left-most operator applies to the least-significant qubit, i.e. that with index 0).
(where in this notation, the left-most operator applies to the least-significant qubit, i.e. that with index 0).
workspace must be a register with the same type (state-vector vs density matrix) and dimensions (number of represented qubits) as qureg, and is used as working space. When this function returns, qureg will be unchanged and workspace will be set to qureg pre-multiplied with the final Pauli product. NOTE that if qureg is a density matrix, workspace will become 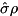 which is itself not a density matrix (it is distinct from
which is itself not a density matrix (it is distinct from 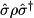 ).
).
This function works by cloning the qureg state into workspace, applying each of the specified Pauli products to workspace (one Pauli operation at a time), then computing its inner product with qureg (for state-vectors) or its trace (for density matrices) multiplied with the corresponding coefficient, and summing these contributions. It therefore should scale linearly in time with the total number of non-identity specified Pauli operators.
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg the register of which to find the expected value, which is unchanged by this function [in] allPauliCodes a list of the Pauli codes (0=PAULI_I, 1=PAULI_X, 2=PAULI_Y, 3=PAULI_Z) of all Paulis involved in the products of terms. A Pauli must be specified for each qubit in the register, in every term of the sum. [in] termCoeffs The coefficients of each term in the sum of Pauli products [in] numSumTerms The total number of Pauli products specified [in,out] workspace a working-space qureg with the same dimensions as qureg, which is modified to be the result of multiplying the state with the final specified Pauli product
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if any code in
allPauliCodesis not in {0,1,2,3} - if
numSumTerms<= 0, - if
workspaceis not of the same type and dimensions asqureg
- if any code in
Definition at line 1210 of file QuEST.c.
References Qureg::numQubitsRepresented, statevec_calcExpecPauliSum(), validateMatchingQuregDims(), validateMatchingQuregTypes(), validateNumPauliSumTerms(), and validatePauliCodes().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ calcFidelity()
Calculates the fidelity of qureg (a state-vector or density matrix) against a reference pure state (necessarily a state-vector).
If qureg is a state-vector, this function computes
![\[ |\langle \text{qureg} | \text{pureState} \rangle|^2 \]](form_174.png)
If qureg is a density matrix, this function computes
![\[ \langle \text{pureState} | \text{qureg} | \text{pureState} \rangle \]](form_175.png)
In either case, the returned fidelity lies in [0, 1] (assuming both input states have valid normalisation). If any of the input Quregs are not normalised, this function will return the real component of the correct linear algebra calculation.
The number of qubits represented in qureg and pureState must match.
- See also
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg a density matrix or state vector [in] pureState a state vector
- Returns
- the fidelity between the input registers
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if the second argument (
pureState) is not a state-vector - if the number of qubits in
quregandpureStatedo not match
- if the second argument (
Definition at line 1191 of file QuEST.c.
References densmatr_calcFidelity(), Qureg::isDensityMatrix, statevec_calcFidelity(), validateMatchingQuregDims(), and validateSecondQuregStateVec().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ calcHilbertSchmidtDistance()
Computes the Hilbert Schmidt distance between two density matrices a and b, defined as the Frobenius norm of the difference between them.
That is, we define the Hilbert Schmidt distance
![\[ D(a, b) = \| a - b \|_F = \sqrt{ \text{Tr}[ (a-b)(a-b)^\dagger ] } \]](form_228.png)
This is equivalent to the square-root of the sum of the absolute value squared of the element-differences of the matrices, i.e.
![\[ D(a, b) = \sqrt{ \sum\limits_i \sum\limits_j | a_{ij} - b_{ij} |^2 } \]](form_229.png)
We caution this may differ by some definitions of the Hilbert Schmidt distance by a square-root.
This function correctly returns the result of the above formulations even when a and b are incorrectly normalised (i.e. are general matrices).
- Parameters
-
[in] a a density matrix [in] b an equally-sized density matrix
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if either
aorbare not density matrices - if
aandhavemismatching dimensions
- if either
Definition at line 1237 of file QuEST.c.
References densmatr_calcHilbertSchmidtDistance(), validateDensityMatrQureg(), and validateMatchingQuregDims().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ calcInnerProduct()
Computes the inner product 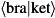 of two equal-size state vectors, given by.
of two equal-size state vectors, given by.
![\[ \langle \text{bra} | \text{ket} \rangle = \sum_i {\text{bra}_i}^* \; \times \; \text{ket}_i \]](form_147.png)
The same qureg may be passed as both bra and ket, though we recommend users check state-vector normalisation with calcTotalProb which employs Kahan summation for greater accuracy. Neither state-vector is modified.
This function returns the correct inner product even if bra and ket are not correctly normalised states.
- See also
- Parameters
-
[in] bra qureg to be the 'bra' (i.e. have its values conjugate transposed) in the inner product [in] ket qureg to be the 'ket' in the inner product
- Returns
- the complex inner product of
braandket
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if either
braandketare not both state-vectors - if
braandketdo not have equal dimensions
- if either
Definition at line 1150 of file QuEST.c.
References statevec_calcInnerProduct(), validateMatchingQuregDims(), and validateStateVecQureg().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ calcProbOfAllOutcomes()
Populates outcomeProbs with the probabilities of every outcome of the sub-register contained in qubits.
This performs no actual measurement and does not modify
qureg.
- For
qubits= {a, b, c, ...},outcomeProbsis populated to
where![\[ \text{outcomeProbs} = \{ \; |\alpha_0|^2, \; |\alpha_1|^2, \; |\alpha_2|^2, \; |\alpha_3|^2, \; ... \; \}, \]](form_137.png)
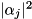 are the probabilities of the respective outcome states (interpreting
are the probabilities of the respective outcome states (interpreting qubitsas ordered least to most significant)
understood in a state-vector![\[ |\dots\textbf{c\,b\,a}\rangle_i \; \; = \;\; |000\rangle, \;\; |001\rangle \;\; |010\rangle \;\; |011\rangle, \;\; \dots \]](form_139.png)
qureg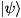 as
as
or in a density matrix![\[ |\psi\rangle = \sum\limits_i^{\text{numQubits}} \alpha_i \; |\dots\textbf{c\,b\,a}\rangle_i \; \otimes \; |\phi\rangle_i, \]](form_140.png)
qureg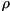 as
as
where![\[ \begin{aligned} \rho &= \sum\limits_{i,j}^{\text{numQubits}} \; \beta_{ij} \; |\dots\textbf{c\,b\,a}\rangle_i\,\langle\dots\textbf{c\,b\,a}|_j \; \otimes \; \mu_{ij} \\ &= \sum\limits_i^{\text{numQubits}} \; |\alpha_i|^2 \; |\dots\textbf{c\,b\,a}\rangle\langle\dots\textbf{c\,b\,a}|_i \;\; + \, \sum\limits_{i \ne j}^{\text{numQubits}} \; \beta_{ij} \; |\dots\textbf{c\,b\,a}\rangle_i\,\langle\dots\textbf{c\,b\,a}|_j \; \otimes \; \mu_{ij}, \end{aligned} \]](form_141.png)
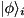 and
and 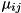 are understood to be the separated states of the remaining qubits.
are understood to be the separated states of the remaining qubits.
outcomeProbsmust be a pre-allocated array of length, which is equivalent to 1<<
numQubits. In distributed mode, every node receives the full list of outcome probabilities.
- Note that the indices in
qubitsneed not be adjacent nor ordered. The order ofqubitsdetermines the order ofoutcomeProbs, wherebyqubitsare treated as increasing significance.
For example, given a
qureginitialised into state-vector![\[ |\psi\rangle = \alpha_0 |000\rangle \;+\; \alpha_1 |001\rangle \;+\; \alpha_2 |010\rangle \;+\; \alpha_3 |011\rangle \;+\; \alpha_4 |100\rangle \;+\; \alpha_5 |101\rangle \;+\; \alpha_6 |110\rangle \;+\; \alpha_7 |111\rangle, \]](form_144.png)
then executing
int qubits[] = {2, 0};int numQubits = 2;qreal outcomeProbs[1<<numQubits];calcProbOfAllOutcomes(outcomeProbs, qureg, qubits, numQubits);would populate
outcomeProbswith![\[ \text{outcomeProbs} = \{ \;\; |\alpha_0|^2+|\alpha_2|^2, \;\; |\alpha_4|^2+|\alpha_6|^2, \;\; |\alpha_1|^2+|\alpha_3|^2, \;\; |\alpha_5|^2+|\alpha_7|^2 \;\; \}. \]](form_145.png)
Since all probability amplitudes of a state-vector are ultimately involved in the output probabilities, calcProbOfAllOutcomes() works as expected for un-normalised states. This is similarly true for density matrices, where all diagonal elements are involved, although only the real values of the diagonal elements will be consulted.
- See also
- Parameters
-
[out] outcomeProbs a pre-allocated array of length 1<< numQubits, which will be modified to contain all outcome probabilities[in] qureg a state-vector or density matrix to study [in] qubits a list of qubits to study [in] numQubits the length of list qubits
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if
numQubits<= 0 - if any index in
qubitsis invalid, i.e. outside [0,qureg.numQubitsRepresented) - if
qubitscontains any repetitions
segmentation-fault - if
outcomeProbsis not pre-allocated - if
outcomeProbscontains space for fewer than 1<<numQubitselements
- if
Definition at line 1176 of file QuEST.c.
References densmatr_calcProbOfAllOutcomes(), Qureg::isDensityMatrix, statevec_calcProbOfAllOutcomes(), and validateMultiTargets().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ calcProbOfOutcome()
Gives the probability of a specified qubit being measured in the given outcome (0 or 1).
This performs no actual measurement and does not change the state of the qubits.
For state-vectors, this function works by summing the absolute-value-squared of every amplitude in the state-vector for which measureQubit = 0. If outcome = 1, it returns 1 minus this value. Hence for unnormalised state-vectors, this result will differ from the absolute-value-squared of every amplitude where measureQubit = outcome.
For density matrices, this function sums the diagonal values (should be real) corresponding to measureQubit = 0 (returning 1 minus this if outcome = 1).
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg object representing the set of all qubits [in] measureQubit qubit to study [in] outcome for which to find the probability of the qubit being measured in
- Returns
- probability of qubit measureQubit being measured in the given outcome
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if
measureQubitis outside [0,qureg.numQubitsRepresented) - if
outcomeis not in {0, 1}
- if
Definition at line 1166 of file QuEST.c.
References densmatr_calcProbOfOutcome(), Qureg::isDensityMatrix, statevec_calcProbOfOutcome(), validateOutcome(), and validateTarget().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ calcPurity()
Calculates the purity of a density matrix, by the trace of the density matrix squared.
Returns 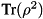 . For a pure state, this =1. For a mixed state, the purity is less than 1 and is lower bounded by 1/2^n, where n is the number of qubits. The minimum purity is achieved for the maximally mixed state identity/2^n.
. For a pure state, this =1. For a mixed state, the purity is less than 1 and is lower bounded by 1/2^n, where n is the number of qubits. The minimum purity is achieved for the maximally mixed state identity/2^n.
This function does not accept state-vectors, which clearly have purity 1.
Note this function will give incorrect results for non-Hermitian Quregs (i.e. invalid density matrices), which will disagree with 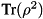 . Instead, this function returns
. Instead, this function returns 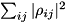 .
.
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg a density matrix of which to measure the purity
- Returns
- the purity
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if either
combineQuregorotherQuregare not density matrices - if the dimensions of
combineQuregandotherQuregdo not match - if
probis not in [0, 1]
- if either
Definition at line 1185 of file QuEST.c.
References densmatr_calcPurity(), and validateDensityMatrQureg().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ calcTotalProb()
A debugging function which calculates the probability of the qubits in qureg being in any state, which should always be 1 for correctly normalised states (hence returning a real number).
For state-vectors 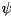 , this is the norm of the entire state-vector (the sum of the absolute-value-squared of every amplitude):
, this is the norm of the entire state-vector (the sum of the absolute-value-squared of every amplitude):
![\[ \sum\limits_i |\psi_i|^2 \]](form_86.png)
and for density matrices 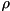 , it is the trace:
, it is the trace:
![\[ \text{Trace}(\rho) = \sum\limits_i \rho_{i,i} \; \]](form_87.png)
For un-normalised density matrices (those directly modified or initialised by the user), this function returns the real component of the trace.
Note this calculation utilises Kahan summation for greater accuracy, and hence is not parallelised and so will be slower than other functions.
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg object representing a set of qubits
- Returns
- the total probability of the qubits in
quregbeing in any state
Definition at line 1143 of file QuEST.c.
References densmatr_calcTotalProb(), Qureg::isDensityMatrix, and statevec_calcTotalProb().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ getAmp()
Get the complex amplitude at a given index in the state vector.
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg object representing a set of qubits [in] index index in state vector of probability amplitudes
- Returns
- amplitude at index, returned as a Complex struct (with .real and .imag attributes)
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if
quregis a density matrix - if
indexis outside [0,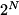 ) where
) where 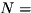
qureg.numQubitsRepresented
- if
Definition at line 939 of file QuEST.c.
References Complex::imag, Complex::real, statevec_getImagAmp(), statevec_getRealAmp(), validateAmpIndex(), and validateStateVecQureg().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ getDensityAmp()
Get an amplitude from a density matrix at a given row and column.
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg object representing a density matrix [in] row row of the desired amplitude in the density matrix [in] col column of the desired amplitude in the density matrix
- Returns
- a Complex scalar representing the desired amplitude
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if
quregis a state-vector, - if
roworcolare outside [0,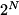 ) where
) where 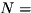
qureg.numQubitsRepresented
- if
Definition at line 949 of file QuEST.c.
References Qureg::numQubitsRepresented, Complex::real, statevec_getImagAmp(), statevec_getRealAmp(), validateAmpIndex(), and validateDensityMatrQureg().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ getImagAmp()
Get the imaginary component of the complex probability amplitude at an index in the state vector.
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg object representing a set of qubits [in] index index in state vector of probability amplitudes
- Returns
- imaginary component at that index
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if
quregis a density matrix - if
indexis outside [0,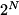 ) where
) where 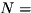
qureg.numQubitsRepresented
- if
Definition at line 925 of file QuEST.c.
References statevec_getImagAmp(), validateAmpIndex(), and validateStateVecQureg().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ getNumAmps()
| long long int getNumAmps | ( | Qureg | qureg | ) |
Returns the number of complex amplitudes in a state-vector qureg.
In distributed mode, this returns the total number of amplitudes in the full representation of qureg, and so may be larger than the number stored on each node. For the latter, refer to Qureg.numAmpsPerChunk.
- See also
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg a state-vecotor
- Returns
- the total number of complex amplitudes representing
qureg.
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if
quregis a density matrix
- if
Definition at line 912 of file QuEST.c.
References Qureg::numAmpsTotal, and validateStateVecQureg().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ getNumQubits()
| int getNumQubits | ( | Qureg | qureg | ) |
Returns the number of qubits represented by qureg.
- See also
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg a state-vecor or density matrix
- Returns
qureg.numQubitsRepresented
Definition at line 908 of file QuEST.c.
References Qureg::numQubitsRepresented.
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ getProbAmp()
Get the probability of a state-vector at an index in the full state vector.
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg object representing a set of qubits [in] index index in state vector of probability amplitudes
- Returns
- realEl*realEl + imagEl*imagEl
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if
quregis a density matrix - if
indexis outside [0,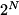 ) where
) where 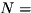
qureg.numQubitsRepresented
- if
Definition at line 932 of file QuEST.c.
References statevec_getProbAmp(), validateAmpIndex(), and validateStateVecQureg().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().
◆ getRealAmp()
Get the real component of the complex probability amplitude at an index in the state vector.
- Parameters
-
[in] qureg object representing a set of qubits [in] index index in state vector of probability amplitudes
- Returns
- real component at that index
- Exceptions
-
invalidQuESTInputError() - if
quregis a density matrix - if
indexis outside [0,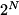 ) where
) where 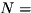
qureg.numQubitsRepresented
- if
Definition at line 918 of file QuEST.c.
References statevec_getRealAmp(), validateAmpIndex(), and validateStateVecQureg().
Referenced by TEST_CASE().